This year, we commemorate the forty-fourth anniversary of the first human lunar landing. By now, the whole world is very familiar with the high-quality Hasselblad snapshots taken by the Apollo astronauts during their voyages. However, 35-mm cameras were also carried on some of the Apollo missions for both surface and orbital imaging. Most of the surface 35-mm images are extreme closeups of the lunar regolith from the Apollo Lunar Surface Closeup Camera (ALSCC; Apollo 11, 12, 14); sometimes called the Gold Camera after its Principal Investigator Thomas Gold. The Nikon camera used on board the Apollo Command Module was equipped with a 55-mm lens and was loaded with either black-and-white or color film. During Apollo missions 16 and 17, black-and-white film was used for dim-light photography of astronomical phenomena and lunar surface targets illuminated by Earthshine. During Apollo 17, color film was used for documenting various activities in the Command Module.
The 35-mm frames are now scanned as part of a joint project between Arizona State University and the NASA Johnson Space Center to scan all of the original Apollo flight films.
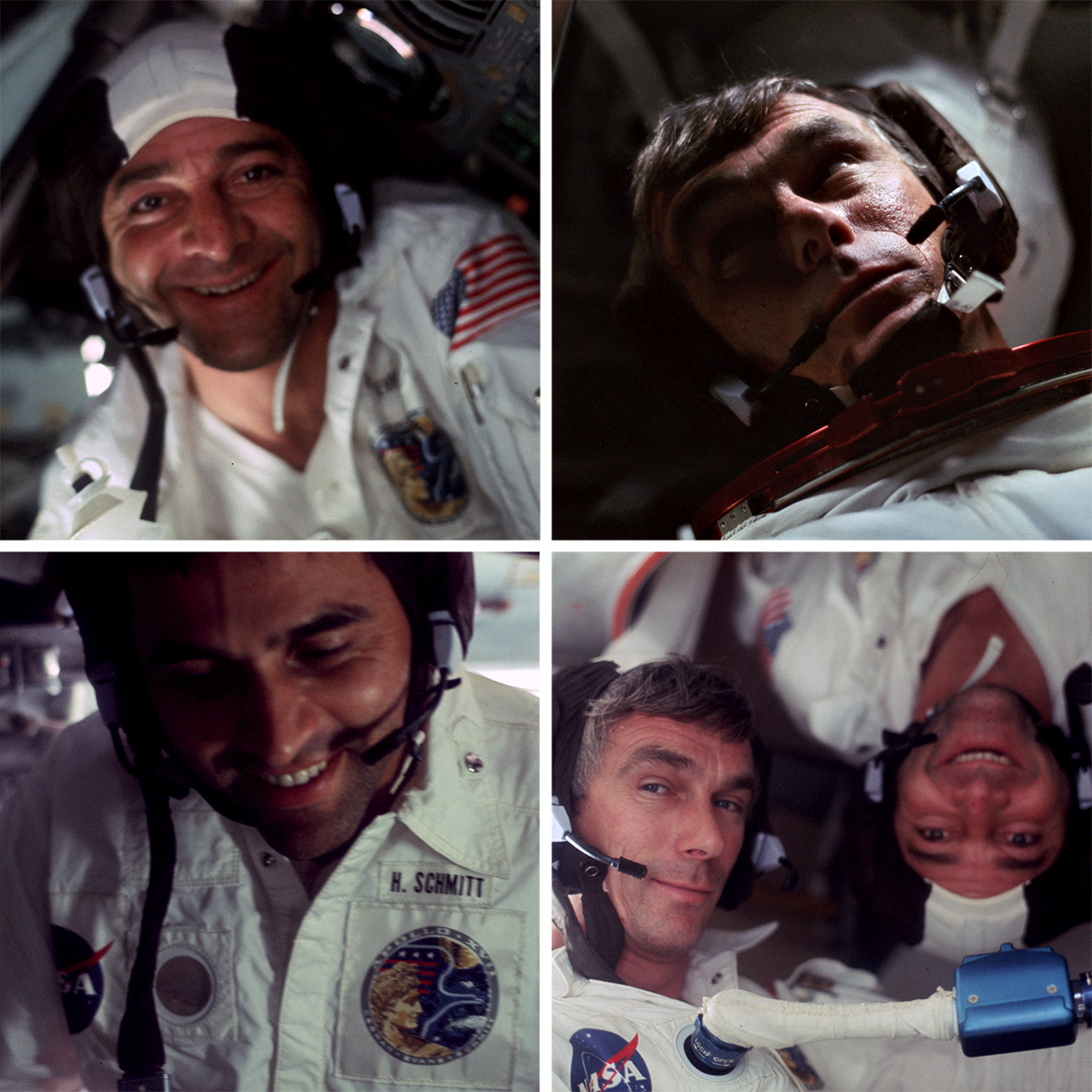
The Apollo 17 crew seems to have had the most fun with the 35-mm format! Gene Cernan, Ron Evans and Jack Schmitt snapped quite a few spectacular black-and-white images showing the view out of the window of their Command Module, the America. Some of these images are a bit grainy, resulting in a very different feeling than the crisp Hasselblad photographs. They also took numerous color candid shots inside the Command Module. It is rare to see such carefree moments during the Apollo missions, but you can feel the relief and happiness after the astronauts so successfully fulfilled their surface mission!
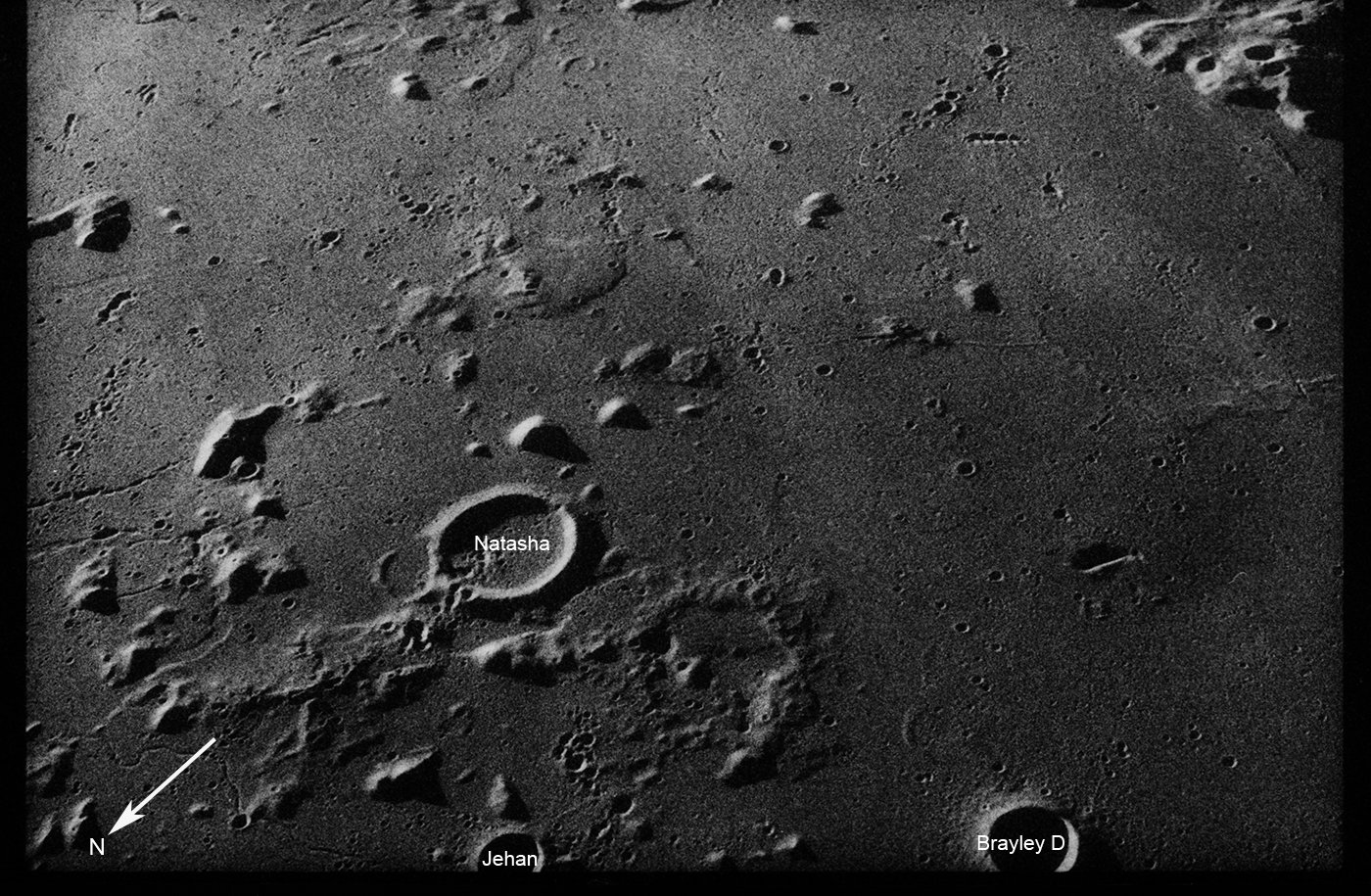
Many of the window shots present an oblique view across lesser known regions of the Moon. The terminator (boundary between night and day) scenes are always captivating. Look closely at the scene below; near the center is a shallow-sloped scallop-shaped rise. Just below and to the right are two other smaller rises - perhaps these are low shield volcanoes? You can dig deeper by visiting the LROC QuickMap browser and see if the NAC images can elucidate what is seen here (Natasha crater is at 19.973°N, -31.157°E).
Relive the incredible adventure that was Apollo, browse the Apollo 35-mm archive and the rest of the Apollo scans (Metric, Pans; Hasselblads to follow next year). While browsing, map out your own next mission to the Moon! The hard part is figuring out where to visit next. Enjoy!
Related Posts:
Project Mercury Photography Now Online
Reiner Gamma Constellation Region of Interest
Published by Mark Robinson on 25 July 2013